Every business consists of Business Processes (BP), a BP refers to a series of structured activities or tasks that are supported by resources, facilities, and information, that interact and produce an outcome to achieve a specific business function or goal. It is often involved multiple departments or functions within the organisation. Processes are everywhere in a business, from onboarding new employees to exist interviews, vendor invoicing, and sales, every business outcome is a result of a sequence of tasks and activities.
Execution and management of BP
For a business to function effectively, its processes need to be clearly specified, consistently executed, and actively managed.
Key aspects of a BP
- Flows of information or documents
- Business processes involve the flow of information and documents, such as purchase orders, invoices, and contracts, within and across different departments.
- The flow of information is essential for coordinating activities, making decisions, and ensuring that all stakeholders are informed and aligned.
- Flows of materials and products
- This include everything from raw materials entering the production process to finished goods being distributed to end customers.
- Efficient management of these flows is critical for meeting customer demand and maintaining production schedules.
- Flows of money
- Financial transactions, such as payments and receipts, are also part of business processes.
- These flows of money must be carefully managed to ensure that the business remains financially healthy, that suppliers are paid on time, and that revenue is collected efficiently and correctly.
Characteristics of a good BP
- Complete
- Include all activities necessary to achieve the business goal.
- Minimal
- Do not include unnecessary activities (cost efficient).
- Well-structured
- Activities are organised in a logical sequence.
- Embedded
- Logically connect with other BPs in the organisation
The outcome of a well-designed business process are:
- Increased effectiveness (value for the customer)
- increased efficiency (less cost for the company)
Levels of abstraction
BPs exist on many different levels of a business.
-
Highest level The core value creation of a business can be depicted as one high-level BP. Source → Produce → Sell → Ship → Provide service
-
Sub processes This BP can be broken-down into smaller sub processes until describing granular activities on the work level. Receive document → Specify quantity → update document → send document to manager for approval → …
Components of a BP
- Activities
- They are specific tasks or actions that need to be performed within a business process to achieve a particular outcome.
- Decisions
- Decisions are points within the BP where a choice is made that influences the subsequent steps in the process.
- Roles
- Roles refer to the individuals or groups responsible for executing specific activities or making decisions within the BP.
- Resources
- People, facilities, or computer systems that are assigned to roles during the execution of the BP.
- Repository
- A repository (i.e. database) is a storage location where data, documents, or information related to the BP are stored and managed.
- Data/information flow
- Data or information flow refers to the movement and flow of data between activities, decisions, roles, and repositories within the BP.
Example - Order fulfilment process
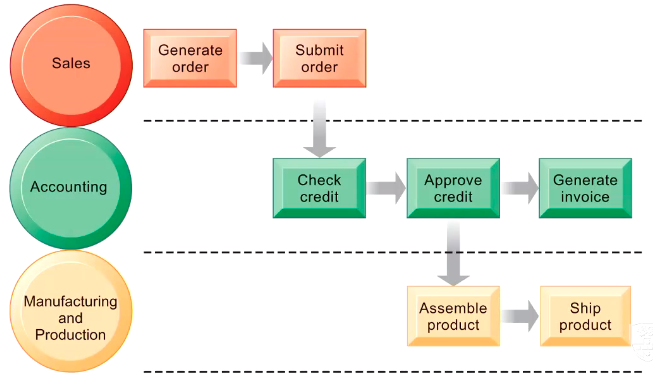 This BP involves multiple departments: sales, accounting, manufacturing and production, with clear roles and logical sequence of steps to ensure a smooth flow.
This BP involves multiple departments: sales, accounting, manufacturing and production, with clear roles and logical sequence of steps to ensure a smooth flow.
- Sales department
- Generate order: The sale department generating an order based on customer demand or a sale request.
- Submit order: Once the order is generated, it is submitted for further processing.
- Accounting department
- Credit check: After the order is submitted, the accounting department checks the customer’s credit to ensure they are eligible for the purchase.
- Approve credit: If the credit is satisfactory, the credit is approved.
- Generate invoice: once the credit is approved, an invoice is generated and sent to the customer.
- Manufacturing and production department
- Assemble product: Upon the credit is approved, the M&P department begins assembling the product.
- Ship product: Once the product is assembled, it is shipped to the customer.
Relationship with information systems
- Information System (IS) supports activities in a BP
- Several activities may use one (integrated) IS
- Activity may have its own IT system
- Activity may use several IT systems
- New BP may require design of new IT system
- New IS facilitate new activities and lead to changes in existing BP
- From “as is” process to “to be” process
- Some processes are automated (run by IT systems), while others are manual.
Back to parent page: Business Information Systems (BIS)