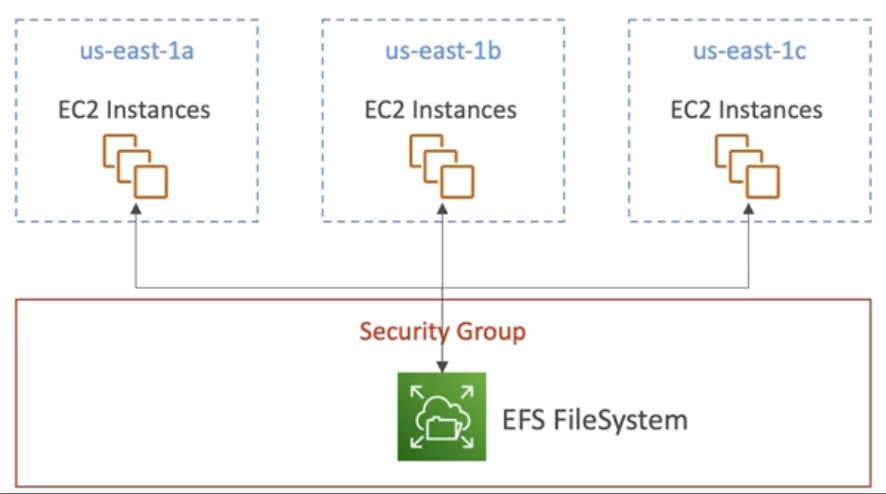
Elastic File System (EFS) is a Managed Network File System (NFS) that can be mounted on hundreds of EC2 instances at a time, this makes it becomes a shared NFS.
EFS only works for Linux EC2 instances in multi-Availability Zone (multi-AZ).
EFS Infrequent Access (EFS-IA)
EFS-IA is a storage class that is cost-optimised for files not accessed every day. Once EFS-IA is enabled, you can define a Lifecycle Policy that automatically moves files that are not accessed for certain days in the standard EFS to the EFS-IA.
EFS VS EBS on availability
EFS and EBS are both storage services in AWS, but they are designed differently.
- EFS EFS is available across multiple AZ and can be mounted to multiple EC2 instances.
- EBS EBS is available in one AZ, it has to reply on EBS Snapshot to transfer data to another AZ.
AWS shared responsibility model for EFS
AWS responsibility
- AWS is responsible for maintaining the infrastructure for storage.
- AWS replicate data for EFS for emergency data recovery.
- AWS replace faulty hardware.
- Ensure employees cannot access user data.
Customer responsibility
- Setup backup of data.
- Setup data encryption.
- Responsible for the data on the drive.
Back to parent node: Cloud Computing
Cloud_computing AWS AWS_CLF-C02 AWS_storage EFS AWS_shared_responsibility
Reference - Udemy Ultimate AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner CLF-C02