The software development methodologies are structured approaches that guide how SDLC is executed.
Waterfall model
Waterfall model is one of the most earliest and most straightforward approaches to software development. Each phase must be completed before the next one can begin.
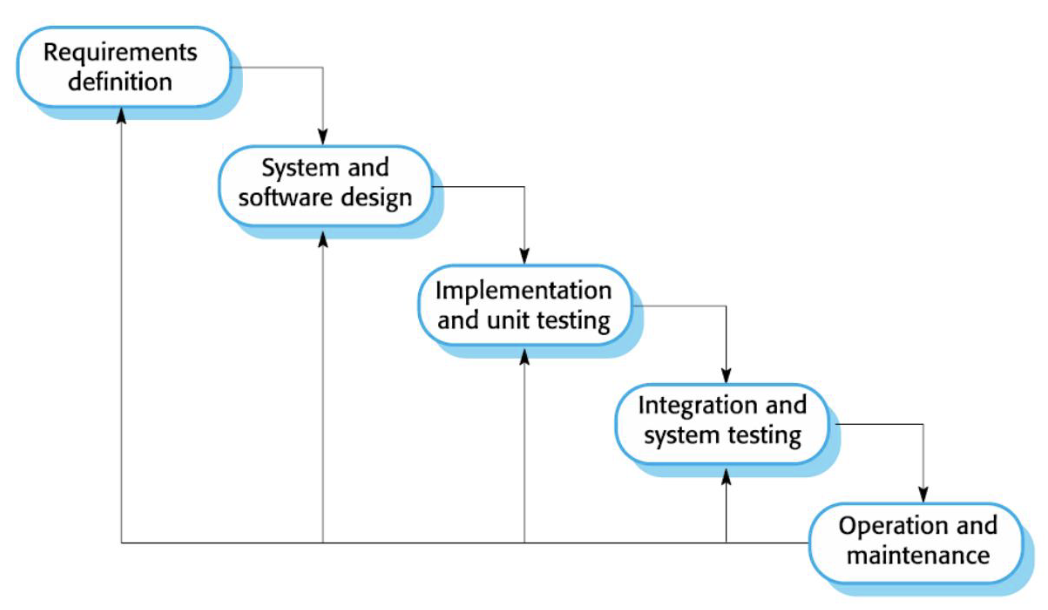
- Requirement analysis and definition
- Gather and document all the requirements for the software project. The output from this phase is the requirement document.
- System and software design
- Design the system architecture based on the gathered requirements. The output in this phase is the design specification document.
- Implementation and unit testing
- Convert the design into code and test it for system components based on the design specification document. The output from this phase is the source code.
- Integration and system testing
- Software components are integrated and the resulting system is tested. The output from this phase is the tested software.
- Operation and maintenance
- Deploy the tested software in the production environment, and provide ongoing support and maintenance for the software.
Advantages Easy to understand and implement, defined deliverables and milestones.
Disadvantages Intensive documenting and planning, discovering issues in later phases should lead to returning to earlier phase. Difficult and costly of accommodating change after the process is underway due to the plan-driven natural of the model.
Agile model
Agile development is an iterative and incremental approach to software development. It is light-weighted, flexible, and people-based rather than plan based. It is more adaptive and responsive to changes. By iterating through the agile development phrases, the team can deliver functional software incrementally, ensuring each release is better than the last.
There is no “standard way” to do requirements in agile development, the requirements are based on user stories. For some key requirements, create some acceptance tests during requirement finalisation.
Scrum
Scrum is an iterative project management methodology that thrives in situations where requirements constantly shift. Scrum is part of the agile movement. It emphasises collaboration, functioning software, team self management, and the flexibility to adapt to merging business realities. Scrum adds a fixed structure with specific rules.
- Fixed-length sprints (1-4 weeks), in agile, iterations can vary in length
- Defined roles
- Scrum master (ensures process runs smoothly)
- Product owner (prioritise work)
- Development team (builds the product)
- Daily stand-up meetings, agile doesn’t require these, but scrum does
- Sprint planning ,sprint reviews, and sprint retrospectives, agile allows flexible feedback loops, but scrum enforces these meetings
V-Model
The V-Model is a software development methodology that emphasises a highly structured, sequential process where each development phase is directly associated with a corresponding testing phase. The name V-Model comes from the V-shaped diagram that represents the process. The V also corresponds to the fact that it is a Verification & Validation diagram. Each activity on the left side needs to be verified.
Note: In the below diagram, in modern software development, these activities are not necessarily sequential. However, the importance of the structuring is in making sure that the corresponding verification and validation stages are complete.
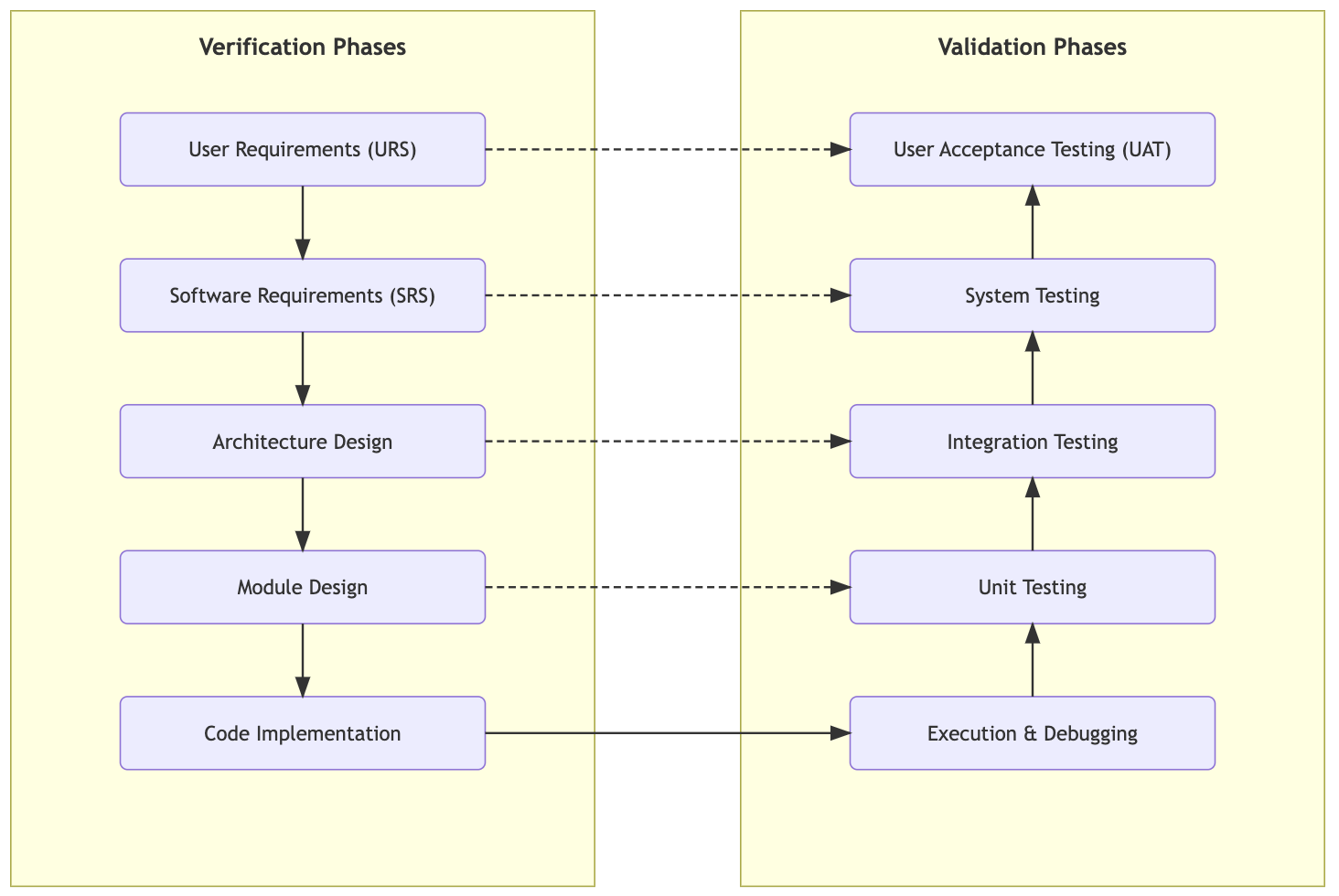
Verification and Validation
Verification
The process of determining whether the products of a given phase of the software development process fulfil the requirements established during the previous phase; Does the software conform to specifications?
| Phase | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| 1. User Requirements Specification (URS) | Defines high-level business needs | User validation sessions, reviews |
| 2. Software Requirements Specification (SRS) | Translates user needs into functional & non-functional requirements | Requirement reviews, traceability checks |
| 3. Architecture Design | Defines system components & interactions | Architecture reviews, modeling validation |
| 4. Module Design | Defines modules, data structures, algorithms, and UI | Design reviews, modeling verification |
| 5. Code Implementation | Writing actual software code | Code reviews, static code analysis |
Validation
The process of evaluating software at the end of software development to ensure compliance with intended usage; Are the users satisfied?
Verification is about having the system right; validation is about having the right system.
Back to parent page: Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
SDLC Software_Development_Methodologies Waterfall_Model SOFT2412 SOFT3202