RIPR model stands for Reachability, Infection, Propagation, Revealability model. It describes the necessary conditions for a fault in a program to be come an observable failure.
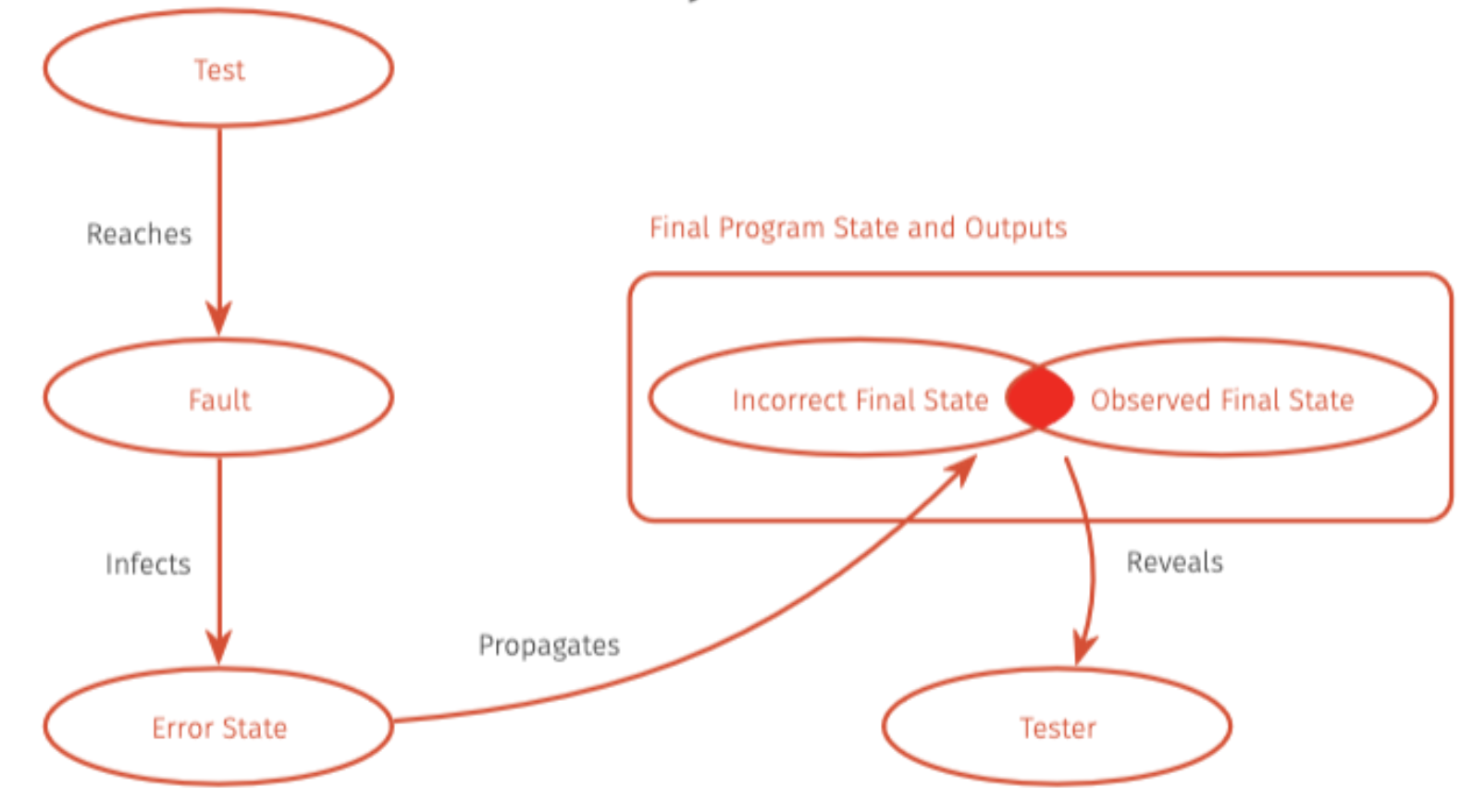
Reachability
- The faulty part of the code must be executed during a testing
- If the fault is never reached, it cannot cause a fault
Infection
- Once the fault is executed, it must cause an incorrect program state (e.g. wrong value in a variable)
- If the state remains correct despite the fault, no failure occurs
Propagation
- If the infected state must propagate to a point where it can affect the program’s output
- The incorrect value must influence some output-related behaviour
Revealability
- The incorrect output must be observable by the tester (e.g. through assertions, logs, or test oracle)
- If no one sees or checks the output, the failure won’t be noticed
Back to parent page: Software Testing
Web_and_App_Development Software_Testing Software_Validation SOFT3202 RIPR_Model