Business objectives
Information System (IS) helps organisations achieve business objectives. Before adopting an IS, we need to understand the business perspectives first. The objectives that organisations aim to achieve through IS are derived from a deep understanding of their industry, the opportunities and risks within it, and the competitive strategies they choose to follow.
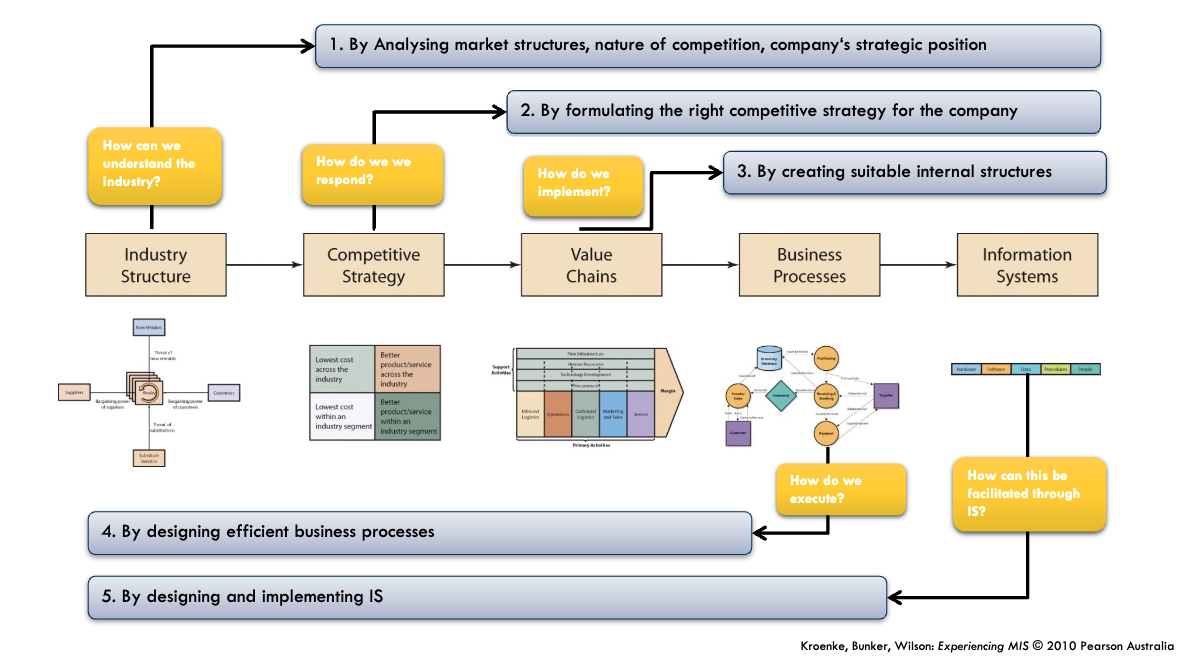
- Examine industry structure The organisations examine industry structure to understand opportunities and risks.
- Devise a competitive strategy Once the opportunities and strategies are understood, organisations create a competitive strategy. The strategy outlines how they will position themselves in the market to gain an advantage over other competitors and factors.
- Design organisational structures and processes Design organisational structures and processes to implement strategy. This involves designing workflows, assigning roles, and structuring departments to efficiently carry out the strategy.
- Design and implement IS to execute processes Finally, once the organisational structures and processes are designed, information systems are introduced to support these processes. The IS can either be designed-in-house or purchased from external providers.
Examine industry structure
An organisation needs to understand the industry and the target market. By performing Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, the organisation can examine current market structure, competitive forces, and external factors influencing profitability and gain a clearer understanding of its strategic position, and the opportunities it can leverage and risks it must address.
Devise a competitive strategy
Based on the analysis of the opportunities, risks, and the industry structure from the Porter’s Five Forces method, organisations can develop appropriate competitive strategies.
Design organisational structures and processes
To execute the competitive strategy, organisation must align their internal structures and processes to deliver products or services. This involves designing workflows, assigning roles, and structuring departments to efficiently carryout the strategy.
Design and implement IS to execute processes
IS enables the automation, management, and optimisation of business processes by integrating IT, procedures, and people. For example, companies might implement an ERP system to manage inventory and supply chain.
Back to parent page: Business Information Systems (BIS)