Having understanding about the users of the system, their needs, preferences, behaviours and the context in which they will interact with the system is the prior step to construct the Information Architecture (IA), it is a important aspect in HCD.
Information collection
This phase involves gathering data and insights about users. The methods below can be adopted for information collection
- Survey
- Interview
- Focus group
- Observation
- Contextual inquiry
- Ethnography
- Studying similar products
Persona
Persona is a fictional, yet realistic, description of different types of users that the system is being designer for. Good persona helps designers to make decisions and remind the team about who will use the product. Persona should focus on UX aspects of interaction, and designing experience that meets their need, rather than on other aspects such as marketing and purchasing behaviours. You should avoid bad persona, such as users that morph to suit the situation, thinking you are the user, and taken account of situation that is very unlikely to occur.
Steps to create persona
- Identify behavioural variables from demographic data. (e.g. activities, attitudes, aptitudes, motivations, skills; if you are designing a fitness APP, relevant behavioural variables might include exercise habits ,fitness goals, etc)
- Identify common pattern by mapping participants to behavioural data. (e.g. In the fitness APP analysis, participants are grouped into segments: fitness enthusiasts, professionals, beginners based on their behavioural data)
- Synthesise and build model, use the findings from previous steps to create persona. (e.g. Beginner Fiona: Age: 30-40; Gender: Female; Occupation: College student; Frequency of Exercises: sporadically)
 After you model the personas, discuss how each persona will behave on your product or system, ensure that your designs reflects the personas.
After you model the personas, discuss how each persona will behave on your product or system, ensure that your designs reflects the personas.
Card sorting
Card sorting is a technique to understand how people classify and categorise things. For example a supermarket checkout machine, if a customer has bought some onions, which category should they select? How about if they have bought some broccoli, courgettes. If customers have to spend a along time searching for the right category, queues will build up. As a method of understanding, card sorting can be a very effective of gaining insight into how people think about things and classify them. There are two types of cards sorts
- Open card sort
- Open card sort starts with blank cards and participants are asked to write down the objects or actions they think are important in some domain.
- Closed card sort
- A closed card sort starts with pre-defined categories and asks participants to place objects into the categories.
The analysts can move between the two different types depending on the questions being addressed.
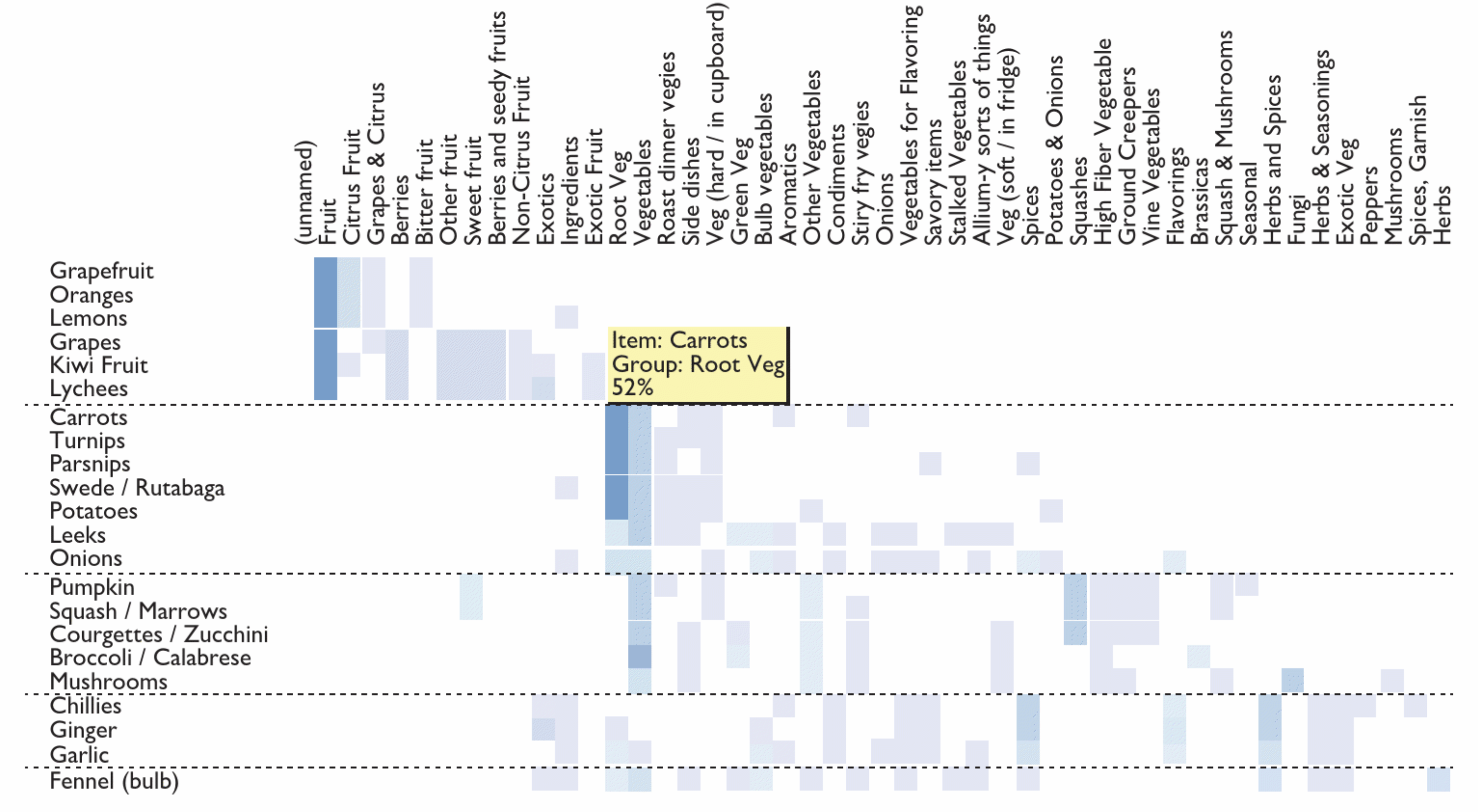
Conduct card sorting
Card sorting can be conducted physically or remotely (using card sorting web application), it can be done by individual participant or groups of participants. If the debrief is conducted during the card sorting, it is a moderated card sorting.
Open card sort
- Invite participants to sort a stack of cards into piles that make sense to them. They should group similar cards together based on their understanding or perception of the content.
- Participants should label each pile using the post-it notes to indicate the category or theme they’ve assigned the cards to.
- Encourage participants to think out loud as they sort the cards, explaining their thought process and reasoning behind their decisions.
Close card sort
- Invite participants to sort the stack of cards into piles according to the pre-defined labels provided. each card should be placed into the category that best fits its content.
- Participants are asked to think out loud as they sort the cards, explaining their though process and reasoning behind their decisions.
Record observations Record the labels and contents of each pile, noting the categories participants create and the items they include in each group.
Back to parent node: Human Computer Interaction (HCI)
Reference:
- Benyon, David. Designing User Experience : A Guide to Hci, Ux and Interaction Design, Pearson Education, Limited, 2019. ProQuest Ebook Central, https://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/usyd/detail.action?docID=5632314.
- https://www.studocu.com/en-au/document/university-of-sydney/computing-2-usability-and-security/info2222-notes-usability/23544359?origin=university-course-page