Abstract data type:
- ADT - Tree
Implementation:
Data_Structure Abstract_Data_Type Tree
In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure. A tree T consists of nodes (vertices) with a parent-child relation.
- If T is non-empty, it has a special node called the root that has no parents.
- Every node
vof T other than the root has a unique parent. - Following the parent relation always lead to the root.
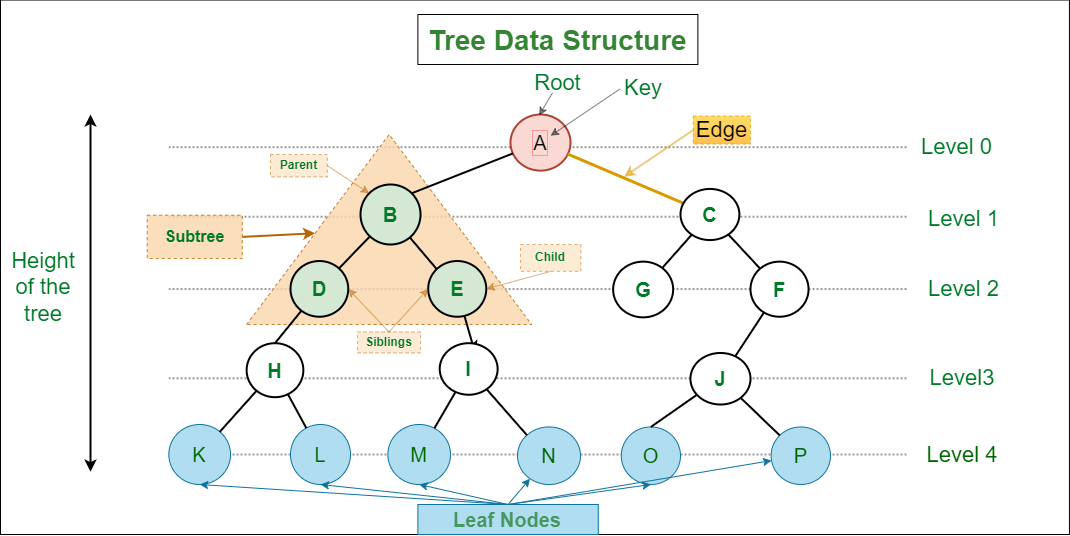
Tree terminology
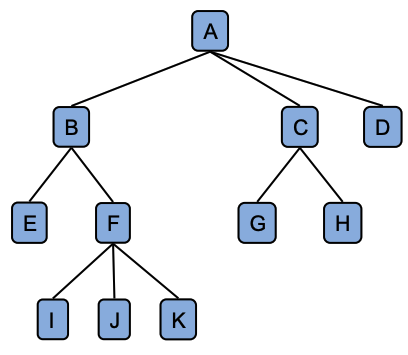
Node classification
- Root
- Node without parent (A)
- Internal node
- Node with at least one child (A, B, C, F)
- External/leaf node
- Node without children (E, I, J, K, G, H, D)
Node relations
- Ancestors
- Parent, grandparent, great-grandparent, etc. (e.g. ancestors of F are A and B)
- Descendants
- Child, grandchild, great-grandchild, etc. (e.g. descendants of B are E, F, I , J, K)
- Siblings
- Two nodes with the same parent are siblings (B, D)
Location concepts
- Depth of a node
- Number of edges present in path from the root node to that node (e.g. depth(F) = 2)
- Level
- Set of nodes with given depth, level starts from 0 (e.g. {E, F, G, H} are level 2)
- Height of a tree
- maximum depth, or the number of edges from the leaf node to a particular node in the longest path. (e.g. the height of node B is 2)
Substructure of a tree
- Subtree
- A smaller tree that is entirely contained within a larger tree, containing a node and all of its child nodes, grandchild nodes, and so on
- Edge
- A connection or link between two nodes
- Path
- A sequence of connected nodes and edges in a graph or tree, representing a route that can be traversed
Operations
- Position as node abstraction
- Generic methods
- integer
size() - boolean
isEmpty() - Iterator
iterator() - Iterable
positions()
- integer
- Access methods
- Position
root() - Position
parent(p) - Iterable
children(p) - Integer
numChildren(p)
- Position
- Query methods
- boolean
isInternal(p) - boolean
isExternal(p) - boolean
isRoot(p)
- boolean
Node ADT
- value: the value associated with this node
- children: set or list of children of this node
- parent(optional): the parent of this node
Traversing trees
A traversal visits the nodes of a tree in a systematic manner.
- pre-order (on the left)
- post-order (on the right)
- in-order (from below)
Preorder traversal
For preorder traversal we print a node when we pass to its left in the cycle
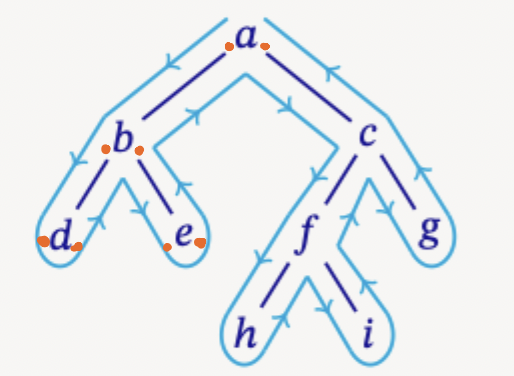 The preorder traversal sequence will be: a, b, d, e, c, f, h, i, g
The preorder traversal sequence will be: a, b, d, e, c, f, h, i, g
void preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (node != null) {
System.out.println(root.value);
traversePreorder(root.left);
traversePreorder(root.right);
}
}Postorder traversal
For preorder traversal we print a node when we pass to its right in the cycle The postorder traversal sequence will be: d, e, b, h, i, f, g, c, a
void postOrderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (node != null) {
traversePreorder(root.left);
traversePreorder(root.right);
System.out.println(root.value);
}
}Inorder traversal
For in-order traversal we print a node when we pass to its bottom in the cycle. The in-order traversal sequence will be: d, b, e, a, h, f, i, c, g
void traverseInorder(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
traverseInorder(root.left);
System.out.println(root.value)
traverseInorder(root.right);
}
}Level order traversal
Level order traversal or sometimes known as breadth-first traversal, visits nodes level by level from left to right. The level-order traversal sequence will be: a, b, c, d, e, f, g, i
List<Integer> levelOrderTravesal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> results = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return result;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode currentNode = queue.poll();
result.add(currentNode.value);
if (currentNode.left != null) {
queue.add(currentNode.left);
}
if (currentNode.right != null) {
queue.add(currentNode.right);
}
}
return result;
}Back to parent node: Data Structures and Algorithms