Prototype is a creational design pattern that allows creating a copy of existing object without depending on the class of the object itself. The cloned objects will not coupled to their concrete classes.
Applicability
- You want to create objects with similar properties and behaviours, and you want to reuse existing objects as template.
- You want to avoid the cost of creating objects from scratch, especially the initialisation of objects is complex or resource-intensive.
- You want to reduce subclassing by cloning prototype instead of asking factory method to make new object. (factory method pattern produces a hierarchy of creator classes that parallel the class hierarchy)
Pros and cons
Advantages
- More efficient when creating objects that are expensive to initialise. The prototype allows for cloning an existing object instead of creating a new one from scratch.
- Hide complexity of creating new instances from the client. Client gets instances without knowing the specifics of how they are created.
Drawbacks
- Deciding between deep and shallow copying can be tricky and requires in-depth understanding of the software system. In some cases there requires a hybrid of shallow and deep copy.
- Might induce complexity during implementation, programmer has be very careful to ensure every necessary attributes are cloned correctly.
Best practices
- Understand deep and shallow copying, use deep copy thoughtfully when objects have reference to other objects, and implement clone method accordingly to avoid unintended sharing of objects between clones.
Approach
- Create a prototype interface or abstract class, define a
clonemethod that will be used to create copies of objects. - Create concrete prototype classes that implement the
clonemethod. These classes should provide a way to create copies of themselves. - In the client code create instances of the concrete prototype classes and use them to create new objects by cloning.
- You can choose to use a
PrototypeRegistrybased on the need.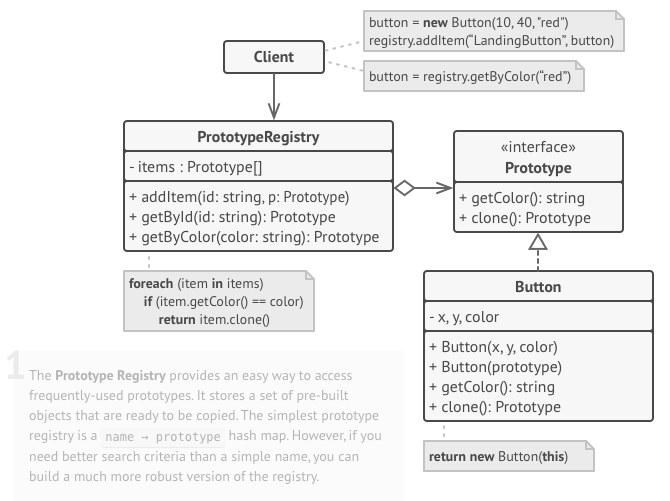
Components
- Prototype (abstract)
- Declares an interface or abstract class with a clone method
- Concrete prototype
- Has a copy constructor that accepts an object of the same class.
- The constructor copy all the fields from the passed object into the newly created instance.
- Implement the clone method for cloning it self.
- Prototype registry
- An optional component that stores a set of frequently used prototypes (the HashMap data structure is often used here).
- The stored prototypes are pre-built and ready to be cloned.
- Client
- Creates new object by asking a prototype to clone itself.
- If there is a prototype registry, the client may ask the registry to obtain the clone.
Example
Consider this example that clones the prototype to create new shape instances.
Prototype
Define a prototype interface.
public interface Cloneable {
Cloneable clone();
}Create concrete prototypes
The concrete prototypes implements the prototype interface. They have a copy constructor that will be used by the clone() method to create a copy of its own.
public class Circle implements Cloneable {
private int radius;
public Circle(int radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
// define a copy constructor that takes an object of the same class
public Cricle(Circle circle) {
// copy all the fields from the parameter object to the new instance
// be careful if deals with attributes that requires deep copy
this.radius = circle.radius;
}
@Override
public Cloneable clone() {
return new Circle(this);
}
}public class Rectangle implements Cloneable {
private int width;
private int height;
public Rectangle(int width, int height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
public Ractangle(Rectangle rectangle) {
this.width = rectangle.width;
this.height = rectangle.height;
}
@Override
public Cloneable clone() {
return new Rectangle(this);
}
}Prototype registry
public class ShapeRegistry {
// contains objects ready to be cloned
private Map<String, Cloneable> prototypes = new HashMap<>();
// create prototypes that is ready to be cloned and used by the client
public ShapeRegistry() {
prototypes.put("circle", new Circle(5)); //default radius
prototypes.put("rectangle", new Rectangle(3, 4)); //default dimensions
}
// the client uses this method to obtain object clone
public Cloneable createShape(String type) {
// create clone of the client desired object
Cloneable prototype = prototypes.get(type).clone();
return prototype;
}
}Client
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShapeRegistry registry = new ShapeRegistry();
// clone a circle
Cloneable clonedCircle = registry.createShape("circle");
// cloen a rectangle
Cloneable clonedRectangle = registry.createShape("rectangle");
}
}Back to parent page: Creational Patterns
Design_Pattern Creational_Design_Patterns SOFT2201 Prototype_pattern