The DNS is the phonebook of the Internet, humans access information online via domain names, such like www.google.com, www.yahoo.com instead of complex number-based IP addresses. The DNS is the technology used on internet to translate human-friendly domain names into IP addresses that can be interpreted by the machine.
History of DNS
Before DNS was developed, domain name lookup was inefficient because it involved looking in a single file on your local system and it is centralised. DNS revolutionised this process by distributing the service. Instead of relying on a single, static file on local system, DNS perform lookup requests via network to distributed remote machines that have the necessary information.
Domain name lookup
Domain name lookup also known today as DNS Resolution, is the process of translating a human-friendly domain names to numeric IP addresses, this process involves accessing databases to look up and fetch the corresponding IP address of the requested domain name recursively from the DNS hierarchy.
DNS resolution
DNS resolution process involves many servers in the DNS infrastructure, more details can be found on DNS Resolution.
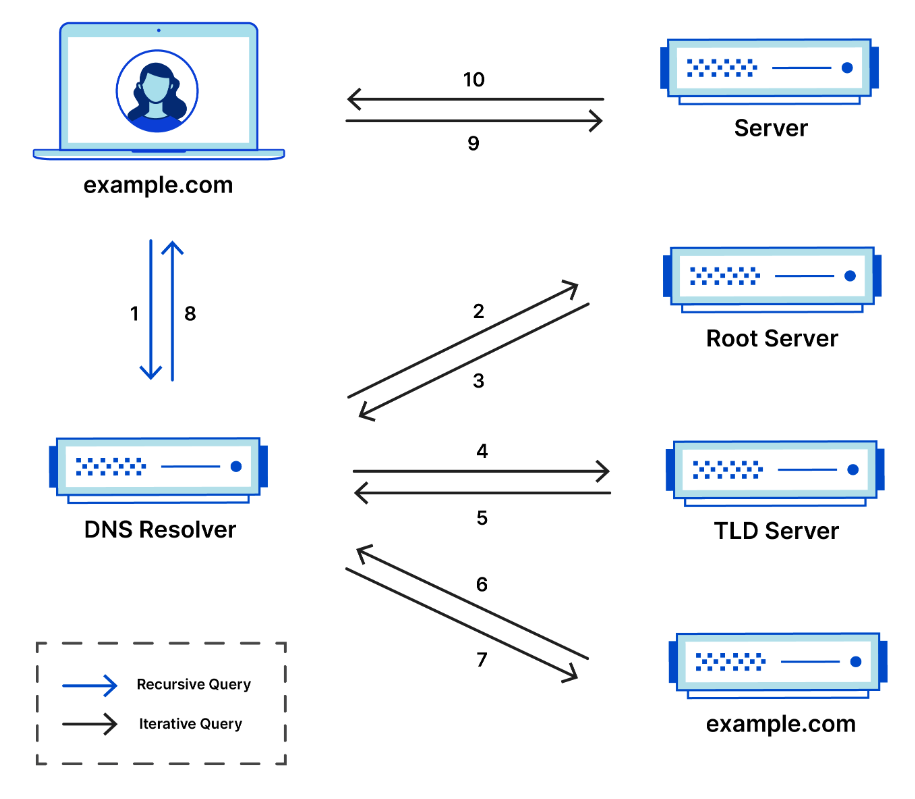
Resolution process
-
Preconfigured Nameserver Your computer is preconfigured with the IP address of a DNS resolver or nameserver.
-
Send query using DNS Protocol When your system wants to resolve a domain name into an IP address, it sends a DNS query to the preconfigured nameserver using the DNS protocol. The DNS protocol sends messages using the UDP.
-
DNS Resolver The preconfigured nameserver receives the DNS query over UDP. It then processes the query, either by providing the IP address directly from its cache or by recursively resolving the query, following the DNS hierarchy until it finds the authoritative DNS server for the requested domain.
-
Response Once the DNS resolver obtains the IP address associated with the domain name you queried, it sends the response (requested IP address) back to your computer using UDP.
Back to parent node: Application Layer
Computer_networks INFO1112 IP_model Application_layer Domain_Name_System_DNS DNS_resolution User_Datagram_Protocol_UDP Internet_Protocol_IP DNS_hierarchy #Nameserver