After “as-is” model, analyse the process model and decide how to improve it. This could incorporate outcome-related improvements, activity-related improvements and resource-related improvements.
Key terms
- Output rate
- Amount of products/services produced by a business process per unit of time
- Throughput rate (AKA flow rate)
- Rate at which units (products/files/requests) flow through a specific activity in the process
- Process capacity
- Maximum output rate of a business process per unit of time
- Capacity utilisation
- Percentage of process capacity that is actually used (output rate/process capacity)
- Lead time
- Average time required for a process to unfold (from start to end)
- Activity time
- Average time required for a specific activity in the process
- Activity resource requirements
- Average unit of resources (man-hours/costs) required for a specific activity in the process
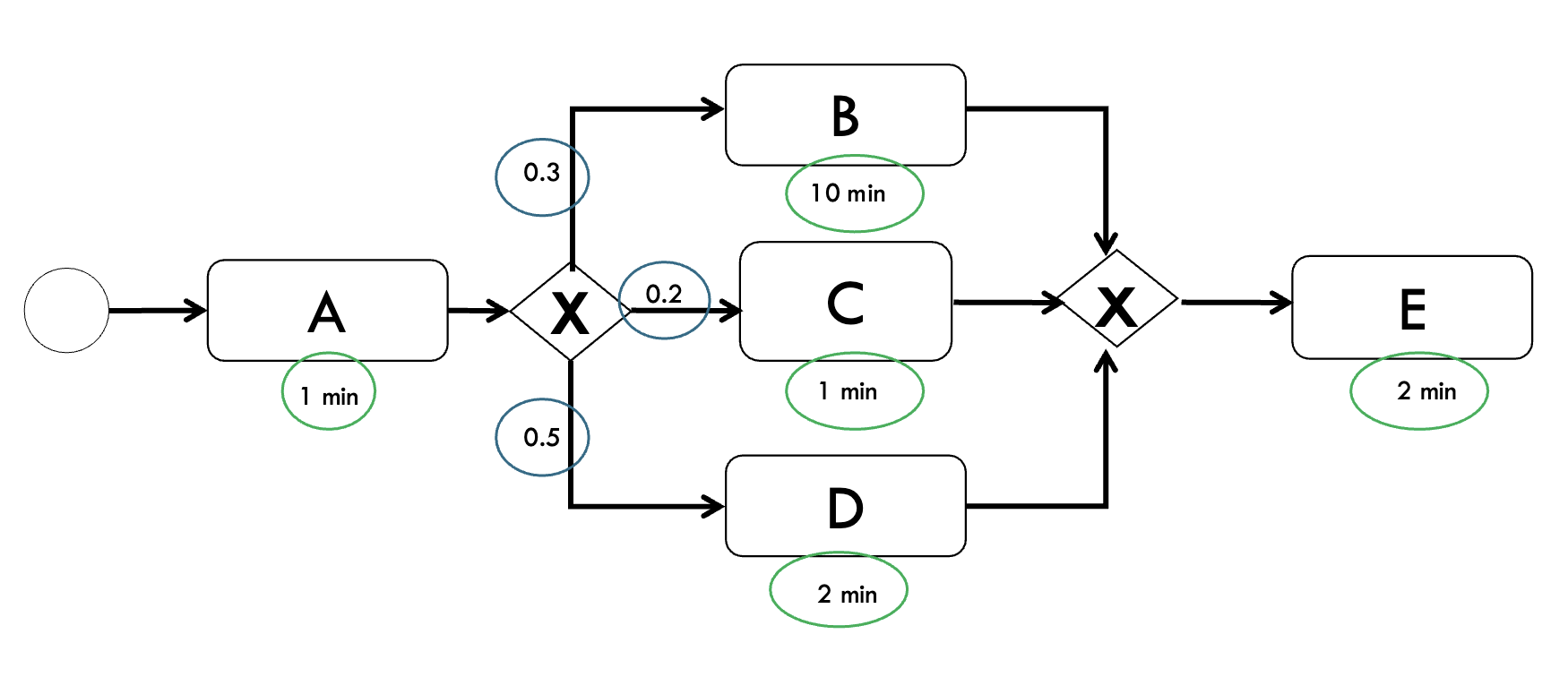
Include additional information in BPD
Include additional information in business process diagram such as:
- Probability options in exclusive gateways
- Activity time
- Activity resource requirements
Outcome-related improvements
Outcomes are not just the final output of the process but the outputs of intermediate activities as well (e.g. an order, an invoice, semi-finished products). There are several methods for outcome improvements.
- Elimination of unnecessary outcomes
- Zero-based start: Every outcome is eliminated and to be re-incorporated, justifications must be made.
- Substitution of outcomes
- Substitute outcomes with more effective/efficient outcomes. E.g. Evaluated receipt settlement → payment without an invoice. Simply count the quantity of goods received and pay based on agreed upon unit price.
- Digitisation of outcomes
- Electronic outcomes are cheaper to store, copy and distribute.
- Harmonisation of outcome
- Horizontal harmonisation
- Standardising the documents or products along the same business process
- e.g. Ensure all departments in a hospital are using the same patient management system.
- Vertical harmonisation
- Standardising and integrating/merging parallel processes for economies of scale
- e.g. Integrating processes from multiple channels (online/offline) or different product lines, such as using a centralised warehouse instead of separate warehouses for different channels
- Horizontal harmonisation
Activity-related improvements
- Elimination of activities
- e.g. Lean management - identify all non-value adding activities and eliminating them
- Moving from a push to a pull principle
- In push principle, activities are driven by forecasts or schedules, work or materials are pushed to the next stage of process without regard to whether the next stage is ready to handle them
- In pull principle, activities are triggered by actual demand or readiness at the next stage. Work or materials are “pulled” through the process only when needed
- Processes that follow a pull principle should never have a bottleneck
- Elimination of bottleneck
- Increase process capacity, sometimes to increase process capacity, the throughput rate has to be increased first
- All activities have equivalent throughput rates is the ideal scenario
- Automation of activities
- Substitute manual activities with the appropriate IT applications
- Parallel routing of activities
- Simultaneous engineering - try to perform sequential activities in parallel
- Substitution of activities
- Replace time-consuming activities
- Include complementary pre-process tasks that reduce lead time for process
- Increase the probability of more efficient pathways
- Exclusive gateways have higher probability lead to more efficient pathways
Resource-related improvements
- Integration of activities
- Making your resources do more
- Job enlargement: integrating 2 related activities of same difficulty. (e.g. data entry operator who enters customer details also verifies the accuracy of the data)
- Job enrichment: incorporate more challenging activities (e.g. data entry operator is given responsibility to analyse the data and produce report)
- Assignment of resources
- Making resources more specific
- e.g. specialisation for complicated tasks, line staff for standard tasks
Back to parent page: Business Process Management (BPM)