RDS is a managed database service for databases use SQL as a query language, it allows you to create databases in the cloud that are managed by the AWS. These databases can be of different kinds:
- Postgres
- MySQL
- MariaDB
- Oracle
- Microsoft SQL Sever
- Aurora (AWS proprietary database)
Why use RDS
While you can deploy databases on EC2 instances, why should you use RDS?
- RDS is fully managed by AWS, provides automated provisioning and OS patching.
- It has continuous backups and can be restored to specific timestamp (Point in Time Restore).
- You will be provided with dashboard for monitoring.
- Read replicas for improved read performance.
- Multi AZ setup for disaster recovery.
- Scaling capability (horizontal and vertical)
- Storage backed by EBS
But you cannot use SSH utility to connect to your database.
RDS solution architecture
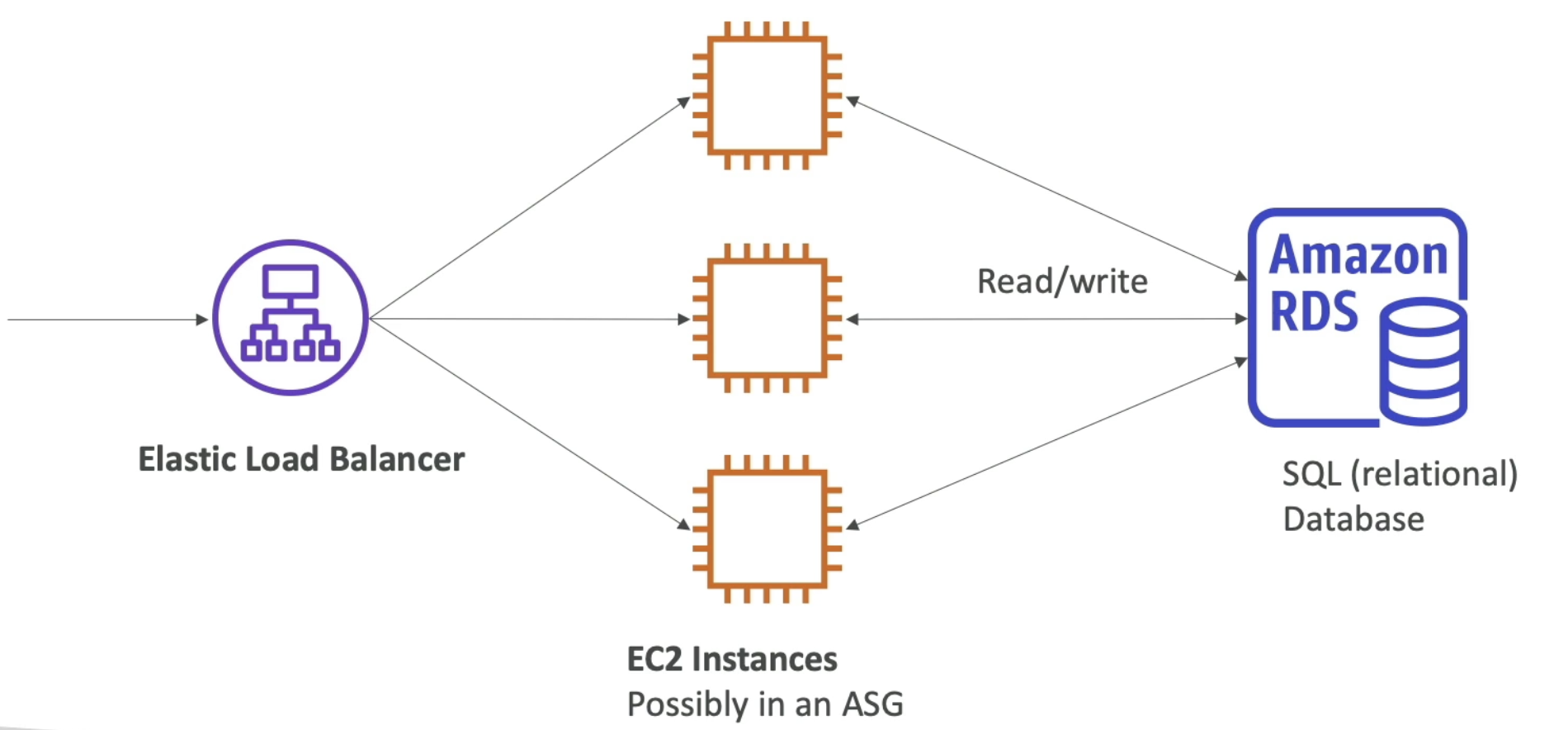 A load balancer is fronting multiple backend EC2 instances which are possible in an ASG. The instances need to store and share structured data in a relational database. Those EC2 instances will read and write data to the Amazon RDS.
A load balancer is fronting multiple backend EC2 instances which are possible in an ASG. The instances need to store and share structured data in a relational database. Those EC2 instances will read and write data to the Amazon RDS.
Table of contents
Back to parent node: Cloud Computing
Cloud_computing AWS AWS_CLF-C02 AWS_database RDS AWS_solution_architecture
Reference* - Udemy Ultimate AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner CLF-C02