Connections between computers fall into two broad classes: Local Area Networks (LAN) and Wide Area Networks (WAN). They can be connected either using a cable or wireless connection (e.g. Wireless-LAN or WLAN). Both LAN and WAN uses packet switching technique.
Local Area Networks (LAN)
The most common form of LAN uses Ethernet technology for interconnection. In Ethernet LAN the data packet is carried in an Ethernet frame.
Wired LAN
The traditional technology for connecting devices is wired LAN, the computers are connected to each other using twisted pair wiring (or more modern optical fibre). The Ethernet frames are transmitted over physical Ethernet cables. Devices are typically connected to ethernet ports on switches or routers.
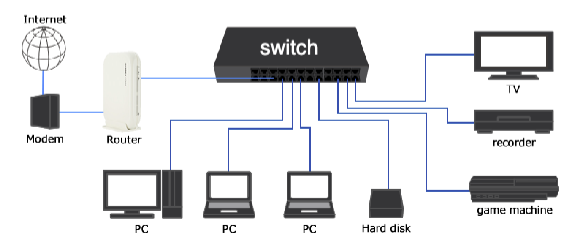
Wireless LAN (WLAN)
A WLAN carries the Ethernet frames using wireless connections. The WLAN works in the same way as wired LAN but instead of using physical cables for interconnections, the devices are connected with radio waves. A wireless router provides wireless connections to devices whose Wi-Fi is ON and within the range of signal. (Wi-Fi is a type of commonly used WLAN connection)
Wide Area Networks (WAN)
A WAN is global and consists of interconnected LANs, the Internet is an example of WAN. The term Internet comes from “Interconnected networks”. Packets are sent from one network to another towards the destination.
Back to parent node: Computer Networks