Value chain is a network of value-creating activities that consist of primary activities and supporting (secondary) activities. These activities bring a product or service from conception, different phases of production, to delivery and beyond.
Generic value chain for manufacturing businesses
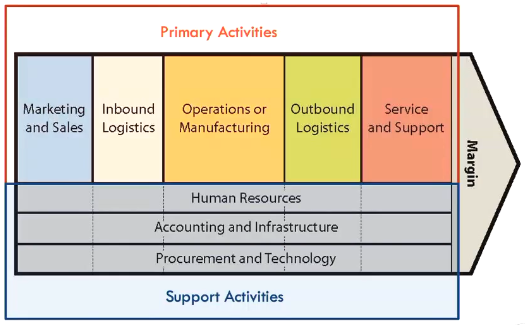
Note
This is a value chain model of a manufacturing-focused business. For service businesses, they won’t have inbound and outbound logistics as they don’t process materials.
Primary activities
Directly contribute to creating or delivering a product/service
- Marketing and sales
- Marketing and sales activities are responsible for promoting the company’s products and generating demand by understanding customer needs, communicating product value, and building customer relationships.
- Added value: Effective marketing and sales ensure that company can reach the right customers, differentiate itself from competitors, and increase revenue through sales.
- Inbound logistics
- Inbound logistics manages the receiving, storage, and transportation of raw materials, components, and supplies needed for production.
- Added value: Inbound logistics ensures that the production process runs smoothly by providing the necessary materials when and where they are needed.
- Operations or manufacturing
- Transform the raw materials and components into finished products.
- Added value: finished goods are ready to sale, directly contributing to company’s core offering to customers.
- Outbound logistics
- Storage and distribution of finished products to customers. It ensures products are delivered on time and in good condition.
- Added value: Ensures that products reach customers efficiently and reliably, enhancing customer satisfaction and optimising costs.
- Service and support
- Service and support activities take place after the sale aim to maintain customer satisfaction and loyalty by addressing issues or providing assistance with product use.
- Added value: Service and support activities enhance the customer experience, leading to greater satisfaction and loyalty. And can provide insight for future product improvements.
Support (secondary) activities
Facilitate the efficiency of primary activities, they indirectly contribute to value creation for the customer.
- Human resources
- Recruitment, training, and employee management processes are designed to ensure the right talent is available to support all value chain activities.
- Accounting and infrastructure
- Support activities include accounting, finance, legal, and general management functions that ensure smooth company operations.
- Procurement and technology
- Procurement involves acquiring the materials, supplies, and vendors the company needs to operate, negotiating prices. This can involve everything from raw materials for manufacturing to office supplies and machinery.
- Technology development involves Research and Development (R&D), and implementing technologies that improve products and processes (e.g. IT systems, automation & robotics).
Business processes in value chain
Business Processes (BP) are essential in executing the activities within a value chain. Each activity in the value chain, whether it is a primary or support activity, is composed of several BPs that ensure the smooth and efficient functioning of organisations.
For example, supplier management is a BP in the inbound logistics. Which is a process for selecting, negotiating, and maintaining relationships with suppliers to ensure timely and cost-efficient procurement of materials.
Back to parent page: Strategy and Competitive Advantage